Last Uploaded: August, 2010
Daito Bunka University
 |
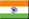
| Exterior of the Central Block with Library. In the foreground, the Air Supply Tower, which draws in natural air from the outside. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Special Features
| Q-1 Indoor Environment |
- Thermal insulation and air tightness provided by external heat insulating wooden sashes (shared)
- Sunlight blocked by deep eaves and vertical louvers (shared)
- Air supply via cool-hot tubes using joint utility ducts (shared)
- Air-conditioning in living areas provided by floor blowers (Central Block with Library)
- Air-conditioning humidity of 40-50% in summer facilitated by desiccant air-conditioning (Central Block with Library)
- On-off control using daylight sensors (No. 3 Block)
- Natural light intake via light shelf and top lights (No. 3 Block)
|
| Q-2 Quality of Service |
- OA floor (Central Block H = 150, No. 3 Block H = 200)
- Ceiling height 3.5m
- Floor height 3.8m
- Rainwater recycling
- Wooden spaces
- Easy-maintenance equipment piping and wiring
|
| Q-3 Outdoor Environment on Site |
- Two quadrangles
- Establishment of a "Spine Space" (semi-external space) as a place for students to gather
- Building height kept low in consideration for residential area to the north of the site
- Use of wood for external walls
- Greenery planted along the road facing the residential area to the north of the site
- Creation of a green quadrangle called the "Forest of Contemplation" to the west of the Central Block and Library
- Green roof
|
| LR-1 Energy |
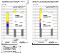
- High values in energy saving plans achieved through simulation, verification and feedback on thermal insulation PAL value: 265.3 MJ/m2/year, which is about 83% of standard value (320 MJ/m2/year)
- Natural ventilation making effective use of draft caused by atrium space (No. 3 Block)
- Natural light intake using light shelf and top lights (No. 3 Block)
- Air supply from cool-hot tubes using joint utility ducts (shared)
- Geothermal heat via hollow structural piles used as a heat source for air-conditioning based on processed external air (measured value COP 4.8)
- Installation of see-through solar panels doubling up as sunlight filters (No. 3 Block)
|
| LR-2 Resources and Materials |
- As building materials, the wood fiber cement boards used for thermal insulation were made from thinning timber sourced in Tokyo.
- Plentiful use of wood is made in the interiors, creating "wooden spaces".
- In the 2nd construction phase, rubble arising from the demolition of existing buildings was buried in the substructure. This helped to reduce industrial waste, while the crevices between the rubble are used for rainwater storage.
|
| LR-3 Off-site Environment |
- Installation of individual operation cooler-heaters (GHP) designed for low NOx and SOx (No. 3 Block)
- Installation of high-efficiency thermal discharge cold and hot water supply designed for use of clean natural gas (Central Block)
- BEMS-compatible central monitoring equipment used to monitor energy consumption (shared)
- Equipment, machinery, galleries, etc., arranged with consideration for noise and vibration
- External walls of buildings finished with external heat insulation and warm wooden finish using teak panels
- Each room designed with openings for natural ventilation
- Rainwater drainage load reduced via rainwater permeation and recycling
|
Other Features
These cases are described based on assessment results obtained using
CASBEE.
CASBEE is a method for rating the environmental performance of buildings using
Building Environmental Efficiency (BEE) as an indicator, which is based on the results of
separate scores obtained for Q-1~Q-3 (Quality) and LR-1~LR-3 (Load Reduction).















 Next Building
Next Building









 | Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.