KAJIMA AKASAKA ANNEX
Facade Engineering
 |
|||
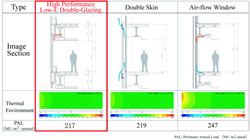
| Window perimeter's thermal environment and energy performance projection | |||
 |
 |
||
High-performance Low-E glass was adopted to achieve often contradicting requirements: superb environmental performance and excellent views from the building. The multi-layered glass structure consists of heat-absorbing glass (12mm) on the exterior and floating glass (8mm) on the inside, with air space (12mm) in between. Low-E sputter coating was applied on the air space side of the floating glass, ensuring minimum heat transfer from the outside while allowing a clear view from the inside of the building.
Task & Ambient Air Conditioning System
 |
|||
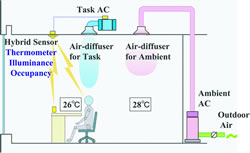
| Task & Ambient Air Conditioning System | |||
 |
|||
The task and ambient air-conditioning system is based on the concept of air-conditioning on demand, i.e., air-conditioning only the necessary areas. The system adopted for this building consists of an ambient air conditioner that gently air-conditions the entire room and supplies outside air, as well as a task air conditioner in each module. The system allows office workers to control the temperature from their seats according to their preferences using the task air conditioner.
Eco-Module
 |
|||
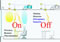
| Hybrid sensor and free address wireless remote thermometer | |||
 |
 |
||
A hybrid sensor was provided in each module in the office space. This sensor consists of 3 separate sensors. The occupancy sensor detects non-occupancy in the room and switches off the lights and air conditioners to prevent wasteful energy consumption. The wireless remote thermometer detects the temperatures at locations close to people and transmits the information to the free address hybrid sensor. The luminance sensor detects the light intensity in the room and automatically controls the luminance of lights to save energy.
Universal Comfort
 |
|||
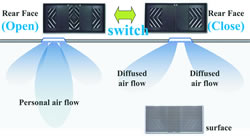
| Universal comfort concept | |||
 |
 |
||
Localized air flow and sudden temperature changes in the multi-split heat pump system may create user discomfort. To solve this problem, an air diffuser was developed to allow users to adjust the air flow and diffusion mode according to individual preference. The air velocity in task areas was determined based on testing and the effectiveness of the system has been continuously verified by monitoring the rate of actual usage.
Natural Ventilation
 |
|||
| Natural ventilation system | |||
 |
|||
As a way to effectively utilize natural energy, the building has a natural ventilation mechanism that uses the outside air when appropriate. The building's passive natural ventilation system uses temperature differences to create air movement vertically through the interior staircases. According to the post-construction testing of the natural ventilation system, it was verified that natural energy accounted for approximately 10% of intermediate load processing.
Previous Building |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Next Building Next Building |
CASBEE is a method for rating the environmental performance of buildings using Building Environmental Efficiency (BEE) as an indicator, which is based on the results of separate scores obtained for Q-1~Q-3 (Quality) and LR-1~LR-3 (Load Reduction).









 | Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.