Last Uploaded: January, 2010
Sakai Gas Building
 |
| Conceptual diagram of a hybrid air conditioning system using natural ventilation and ceiling fans |
 |
 |
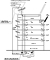 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Special Features
| Q-1 Indoor Environment |
- PMV sensors are installed to enable temperature control within a comfortable temperature range.
- The natural air intake chamber is provided with the means to prevent external noise from entering.
- The air conditioning zone is divided according to direction, interior, and perimeter.
- Environmental adjustment mechanisms by the ceiling fans that are individually controllable.
- The common use space which allows sufficient natural light in by segmenting the core.
|
| Q-2 Quality of Service |
- Reliability is improved by micro gas turbine cogeneration.
- OA floor: 200 mmH
- Power supply capacity: 50 VA/m2
- Ceiling height: 2.8 m
- Story height: 4.3 m
- High earthquake resistance
- A dual structure is used for the power supplies and heat sources for important equipment.
- Use of rainwater
- Dedicated EPS for telecommunications
- Vending machine space is provided for refreshment for nonsmokers in addition to a separate space for smoking.
|
| Q-3 Outdoor Environment on Site |
- Matching with urban axes, vertical faces reflecting the sky, greening of the site, and the construction and maintenance of a small parks.
- Greening of the exterior and the roof, water-permeable pavement, heat exhaust units concentrated on the roof
- Greening of the exterior and the roof was actively promoted to maintain the environment around the site.
|
| LR-1 Energy |
- As a cooling function, ceiling fans are used to extend natural ventilation time.
- As a cooling function, ceiling fans are used to achieve comfortable air conditioning at 28°C in summer.
- Natural ventilation-based hybrid air conditioning, night purge, and daylight usage control are adopted.
- Various energy-saving systems are used for air conditioning, ventilation, lighting, and elevators.
- A BEMS is used to perform in-depth monitoring by system and by unit.
- Monitoring data is used to conduct commissioning at the operation stage.
|
| LR-2 Resources and Materials |
- Rainwater is used as water for miscellaneous use.
- A water-saving plunger and toilets are utilized.
- Pavement bricks made from sewage sludge and an OA floor using waste glass and blocks are adopted.
- Building frames and finishing materials are easy to separate, and so are interior materials and equipment.
- An absorption type chiller heater is used as the main heat source with ODP planned to be 0.
- Heat exhausted from the CGS is used for desiccant air conditioning systems, exhaust heat recovery/absorption type chiller heaters, heating systems, and hot water supply systems.
|
| LR-3 Off-site Environment |
- The main units are low noise models and are installed on the roof. Screens are used for the exterior.
- Exhaust air from the kitchen is released through the roof. A kitchen garbage disposal unit is installed on the roof for deodorization.
- The corners of the building are shaved in accordance with the findings of simulations and theoretical research.
- Exterior walls of low solar absorptivity are used. The layout of the building is suitable for the usual wind direction. Water-permeable pavement is used.
|
Other Features
- A piping antifriction agent is sealed in the air conditioning piping system to save conveyance power.
- Perimeter loads are locally treated by adopting simple air flow windows.
- Hybrid outside air treatment using a combination of a desiccant and a total heat exchanger.
- In-depth post-operation performance verification was conducted to confirm each energy-saving technology.
|
These cases are described based on assessment results obtained using
CASBEE.
CASBEE is a method for rating the environmental performance of buildings using
Building Environmental Efficiency (BEE) as an indicator, which is based on the results of
separate scores obtained for Q-1~Q-3 (Quality) and LR-1~LR-3 (Load Reduction).























 Next Building
Next Building









 | Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2008 Institute for Building Environment and Energy Conservation, All Rights Reserved.